给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

**输入:**head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
**输出:**返回索引为 1 的链表节点
**解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
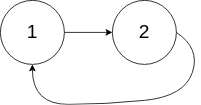
**输入:**head = [1,2], pos = 0
**输出:**返回索引为 0 的链表节点
**解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

**输入:**head = [1], pos = -1
**输出:**返回 null
**解释:**链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
定义fast与slow指针,fast指针每次前进两个结点,slow指针每次前进一个结点。
设$x$为头节点到环入口距离,$y$为从环入口到fast与slow相遇节点的距离,$z$为相遇节点到环入口距离。
则相遇时,fast走过$n(y+z)+x$个结单,slow走过$x+y$个结点,其中$n$为fast在环内绕的圈数。
fast走过的结点数是slow的两倍:$2(x+y) = n(y+z) + x$
整理得:$x = (n-1)(y+z) +z$
当$n=1$,$x=z$,此时可以在相遇节点与头节点分别设置指针index1与index2。它们每次走一个结点,相遇处即为环入口。
$n>1$时同理。
![[Pasted image 20250405130912.png]]
1 | |